Ahead-looking: Rising demand for AI-driven information facilities is straining the power grid. Repurposed electrical automobile batteries supply a promising answer, storing renewable power extra effectively whereas decreasing waste. This rising know-how might reshape how we energy the digital age.
Redwood Power, a Redwood Supplies enterprise, goals to change how individuals use lithium-ion batteries. As a substitute of sending batteries from electrical automobiles straight to recycling, the corporate offers them a second life, extending their use earlier than reclaiming minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The corporate’s engineers and technicians discovered that many batteries nonetheless maintain over half their authentic capability after they’re now not appropriate for vehicles. As a substitute of breaking them down instantly, the workforce repurposes these batteries as stationary power storage items.
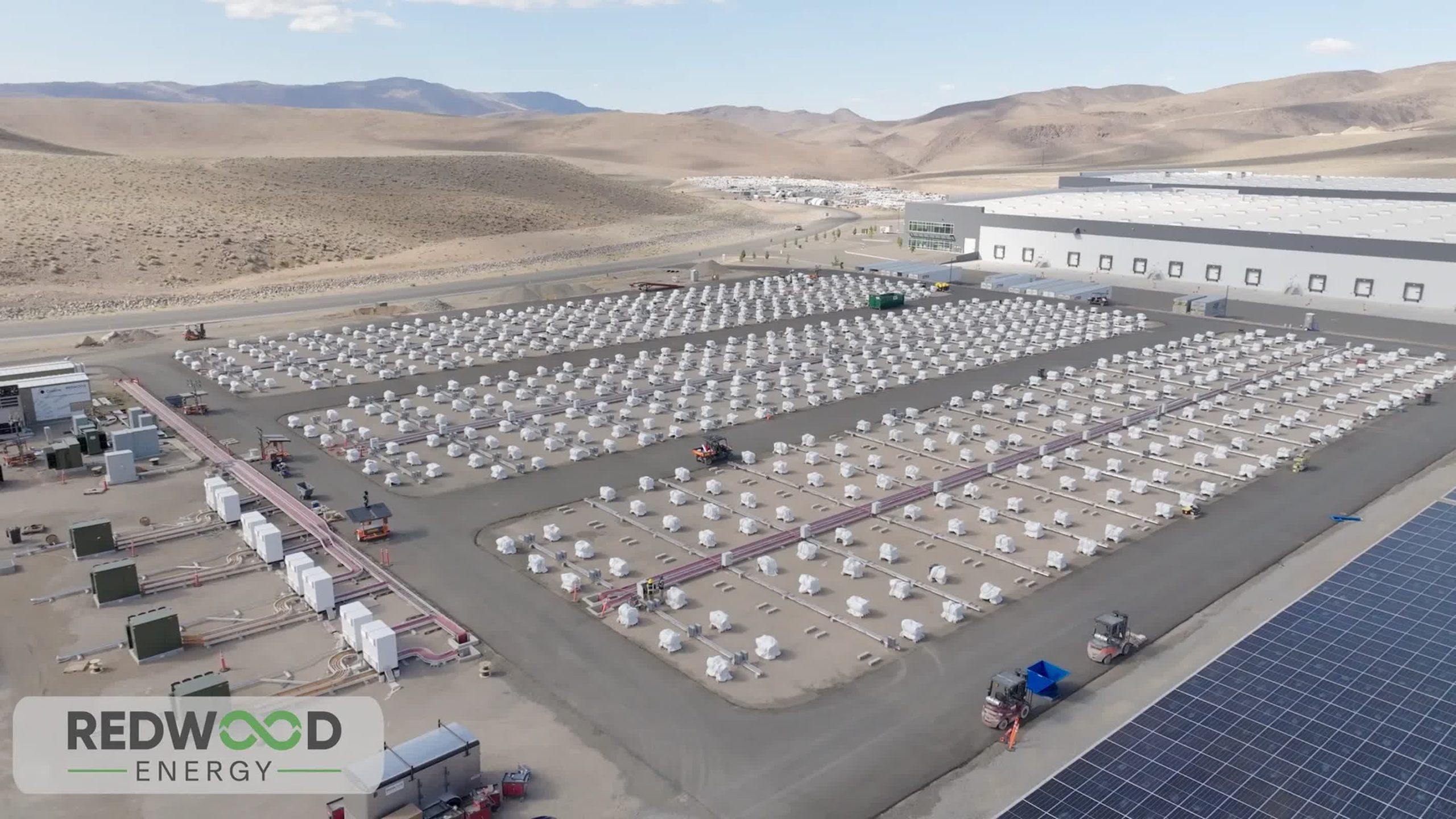
Redwood runs a nationwide logistics community that collects over 70 p.c of North America’s used battery packs annually. Technicians conduct superior diagnostics to find out whether or not to reuse a battery or recycle it. People who go are assembled into modular power storage programs, no matter producer or chemistry. Redwood’s management system allows these various packs to work collectively, storing and delivering electrical energy on demand.
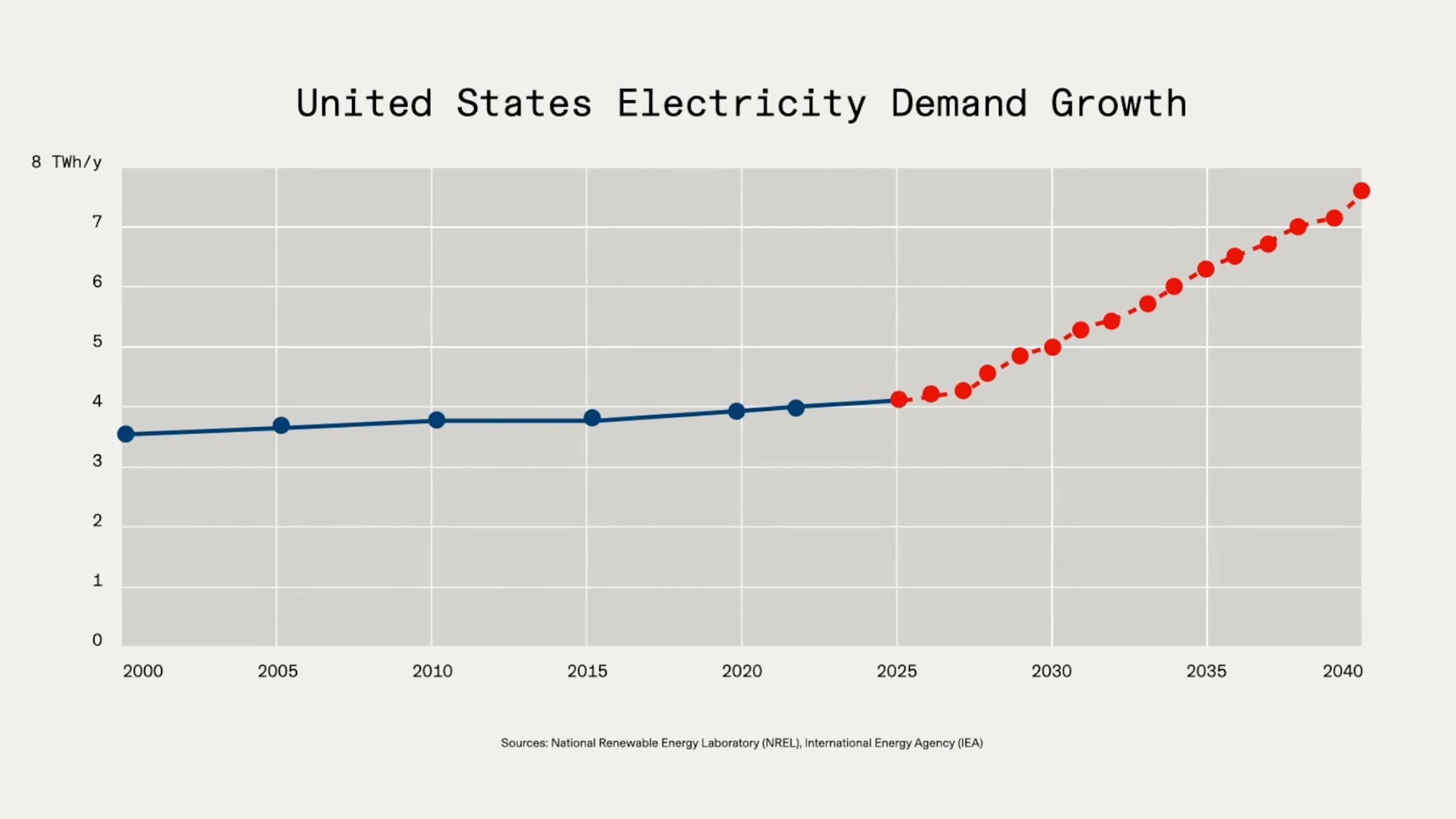
Repurposed battery programs are a pure match for contemporary information facilities, that are increasing quickly with the rise of AI and cloud computing. These services devour huge quantities of energy, and analysts forecast a big surge in demand. By 2028, information facilities might use as much as 12 p.c of all electrical energy generated within the US. Conventional grid growth and battery manufacturing cannot sustain, and whereas wind and photo voltaic are clear, they’re intermittent. Giant-scale battery storage helps fill the hole by storing extra power when it is accessible and releasing it when it is not.
A brand new microgrid constructed close to Reno, Nevada, with AI infrastructure firm Crusoe, reveals this method in motion. The set up delivers 12 megawatts of energy and 63 megawatt-hours of storage, making it the biggest second-life battery deployment on this planet – and the biggest microgrid in North America. Tons of of repurposed EV batteries, paired with photo voltaic panels, now energy an information heart working 2,000 GPUs. The whole challenge got here collectively in simply 4 months, far quicker than the years it typically takes to safe new grid connections or construct an influence plant.
It really works nicely as a result of stationary storage places much less pressure on batteries than powering a transferring automobile. Electrical automobile batteries should deal with speedy acceleration and fixed biking, however microgrids function at slower discharge charges and decrease frequencies. Consequently, batteries now not suited to vehicles can nonetheless carry out reliably on this position – typically at half the price of new lithium-ion programs, with related efficiency.
Redwood’s method closes the battery lifecycle loop: after repurposing batteries in microgrids, the corporate ultimately recycles them to get well vital minerals and feed the availability chain. This mannequin has broad potential. With over 5 million electrical automobiles on US roads and greater than 100,000 retiring annually, the pool of reusable batteries is rising quick. Redwood estimates that these second-life batteries might ultimately provide half or extra of the complete power storage market.
JB Straubel, founding father of Redwood Supplies and co-founder of Tesla, calls this just the start. He instructed Bloomberg the corporate already has sufficient reusable batteries to energy microgrids supplying over 1,000,000 houses for an hour, with plans for initiatives ten instances bigger than its present deployment.