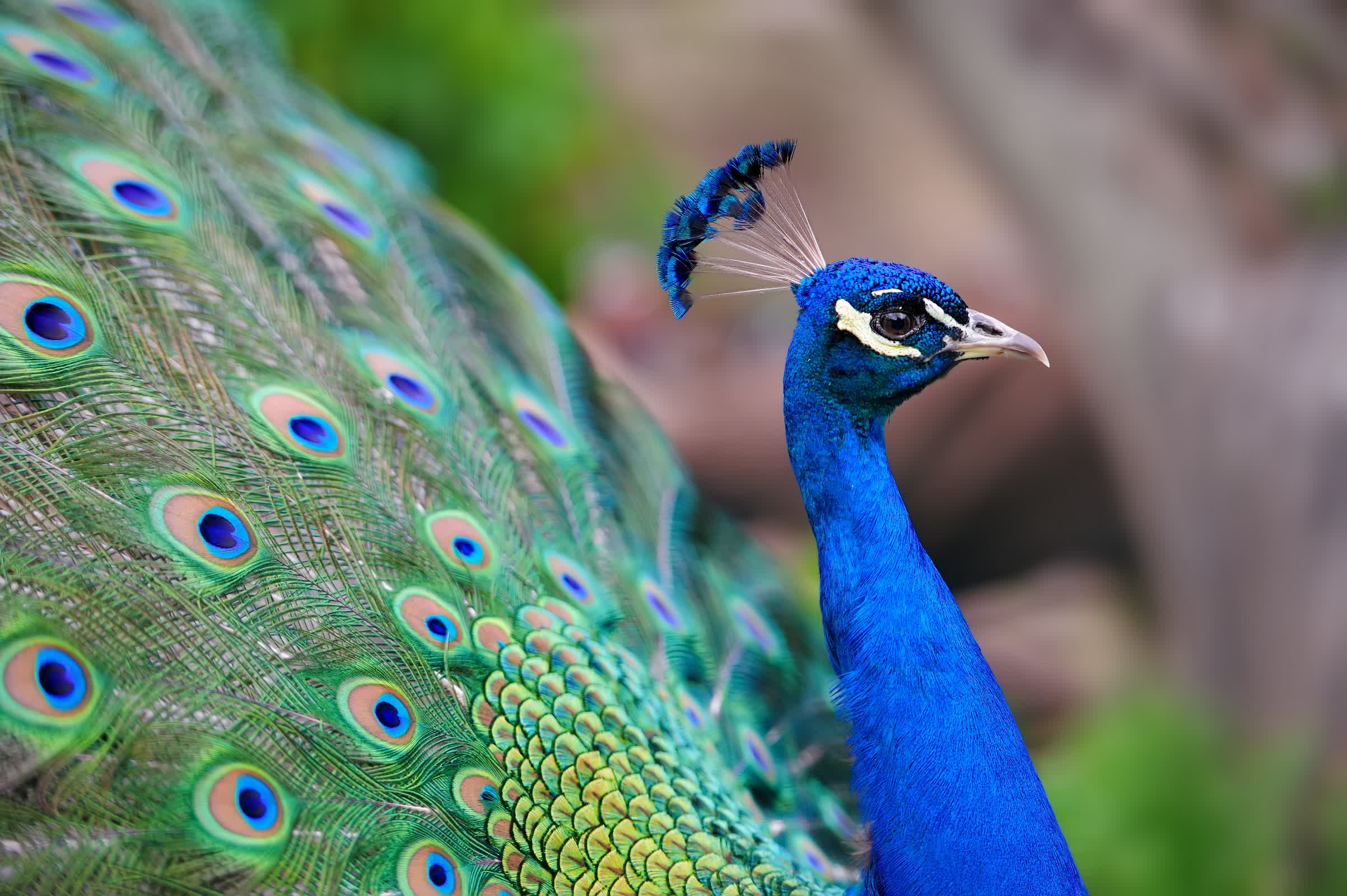
TL;DR: Scientists have lengthy been fascinated by the colourful colours and complex constructions discovered within the feathers of birds just like the Indian Peafowl (generally often known as the peacock). A brand new examine has make clear a shocking property of those iconic tail feathers: their capability to behave as tiny laser resonators when infused with a standard fluorescent dye.
The analysis, carried out by researchers from a number of US universities and printed in Nature, got down to discover the conduct of peacock feather barbules – microscopic constructions that assist create the chook’s well-known shimmering eyespots – when handled with the laser dye rhodamine 6G. The purpose was to find out if mild emitted from these dyed feathers would reveal insights in regards to the underlying organic construction, and whether or not the colourful photonic crystals within the feathers themselves may function suggestions mechanisms to provide laser mild.
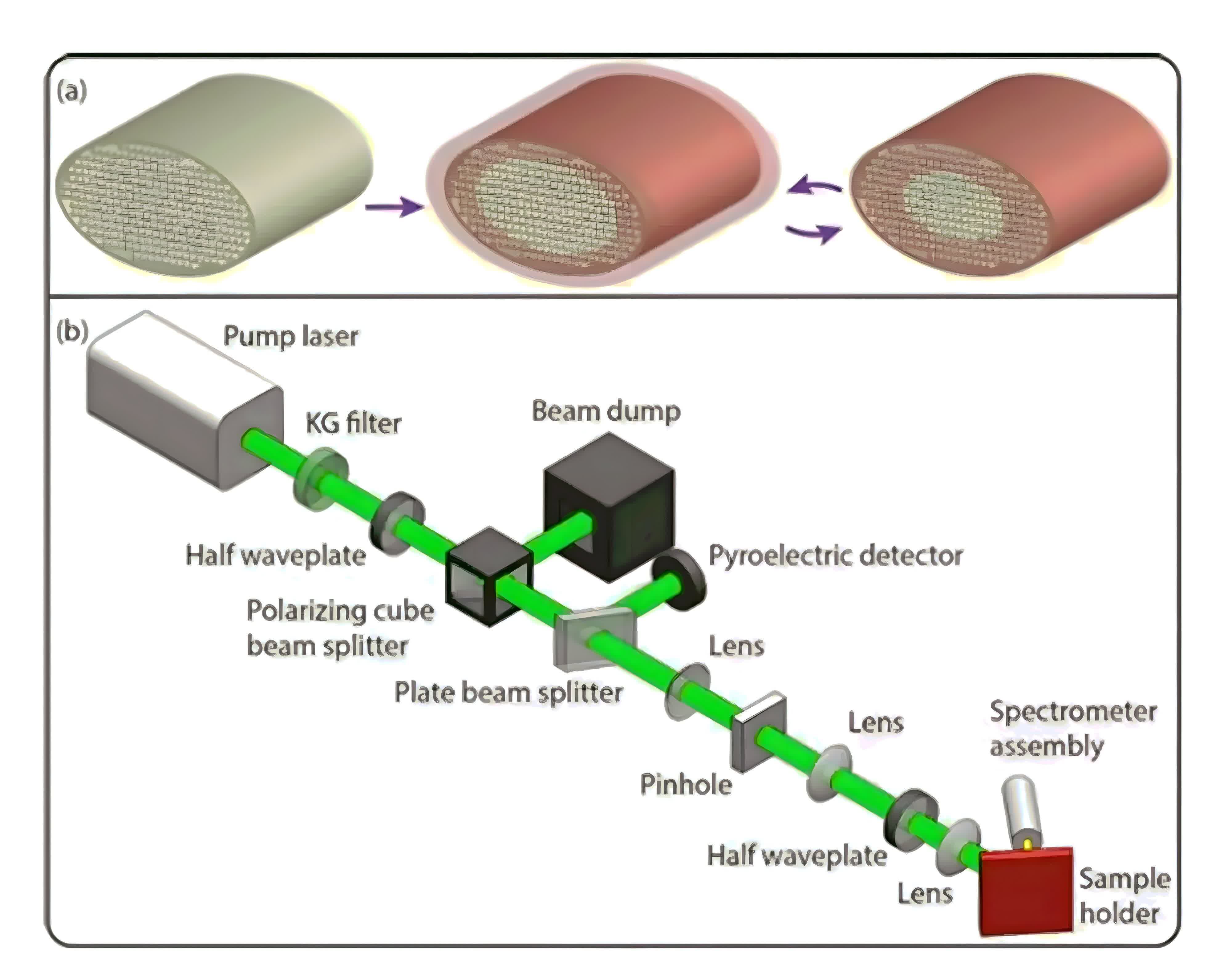
To conduct the experiment, scientists obtained pure peacock feathers, fastidiously minimize them to isolate the eyespot space, and repeatedly wetted and dried particular areas with an answer containing rhodamine 6G. This dye is well-known for its vibrant fluorescence when uncovered to inexperienced laser mild. Utilizing pulses from a inexperienced laser, the workforce illuminated the ready feathers and picked up the emitted mild by means of a specialised spectrometer system.
Preliminary outcomes confirmed that merely staining the feathers as soon as was not sufficient – laser emission solely appeared after a number of cycles of wetting and drying. This instructed that each the dye and solvent should deeply penetrate the barbules and presumably alter the microstructure for the impact to manifest.
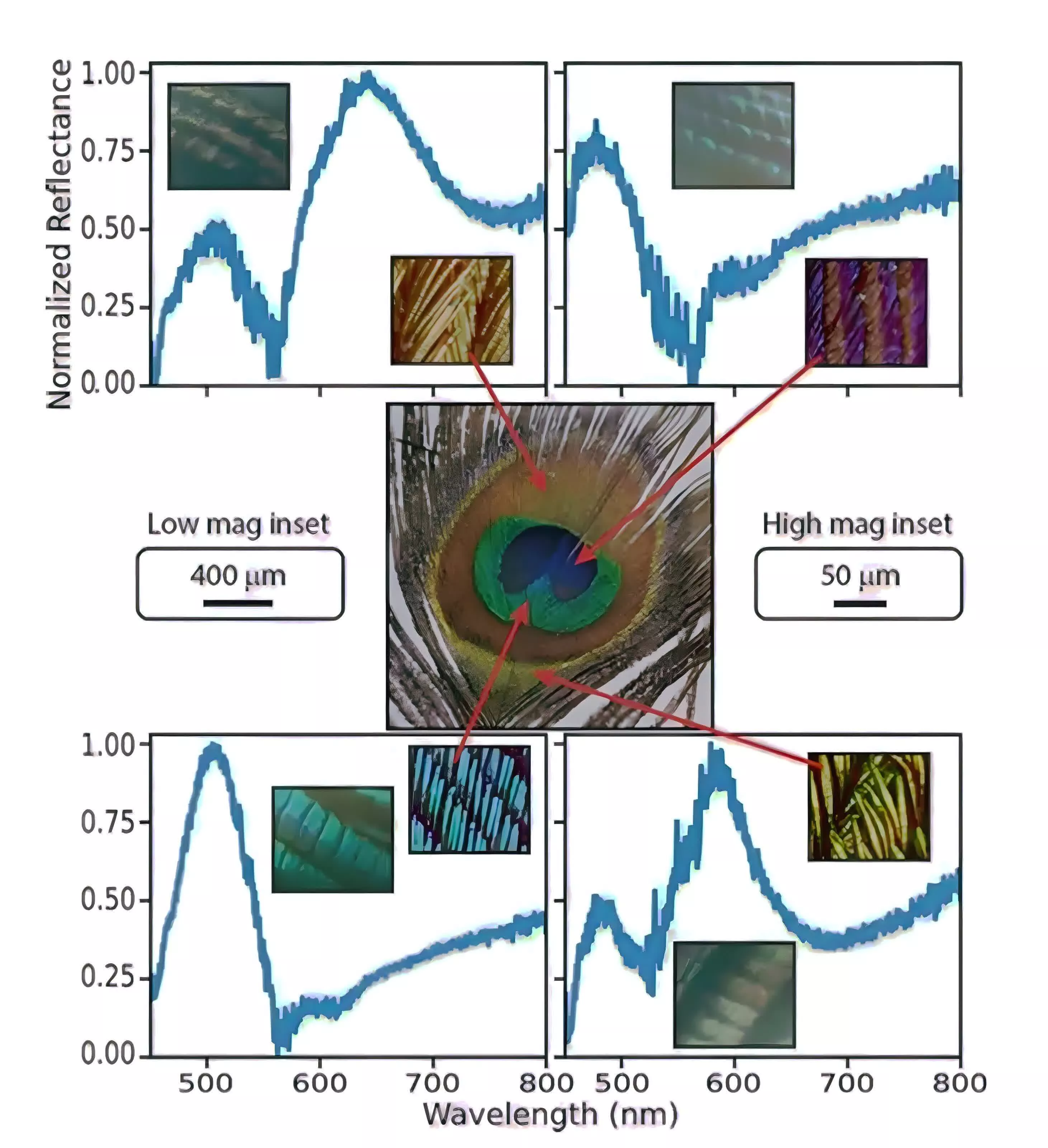
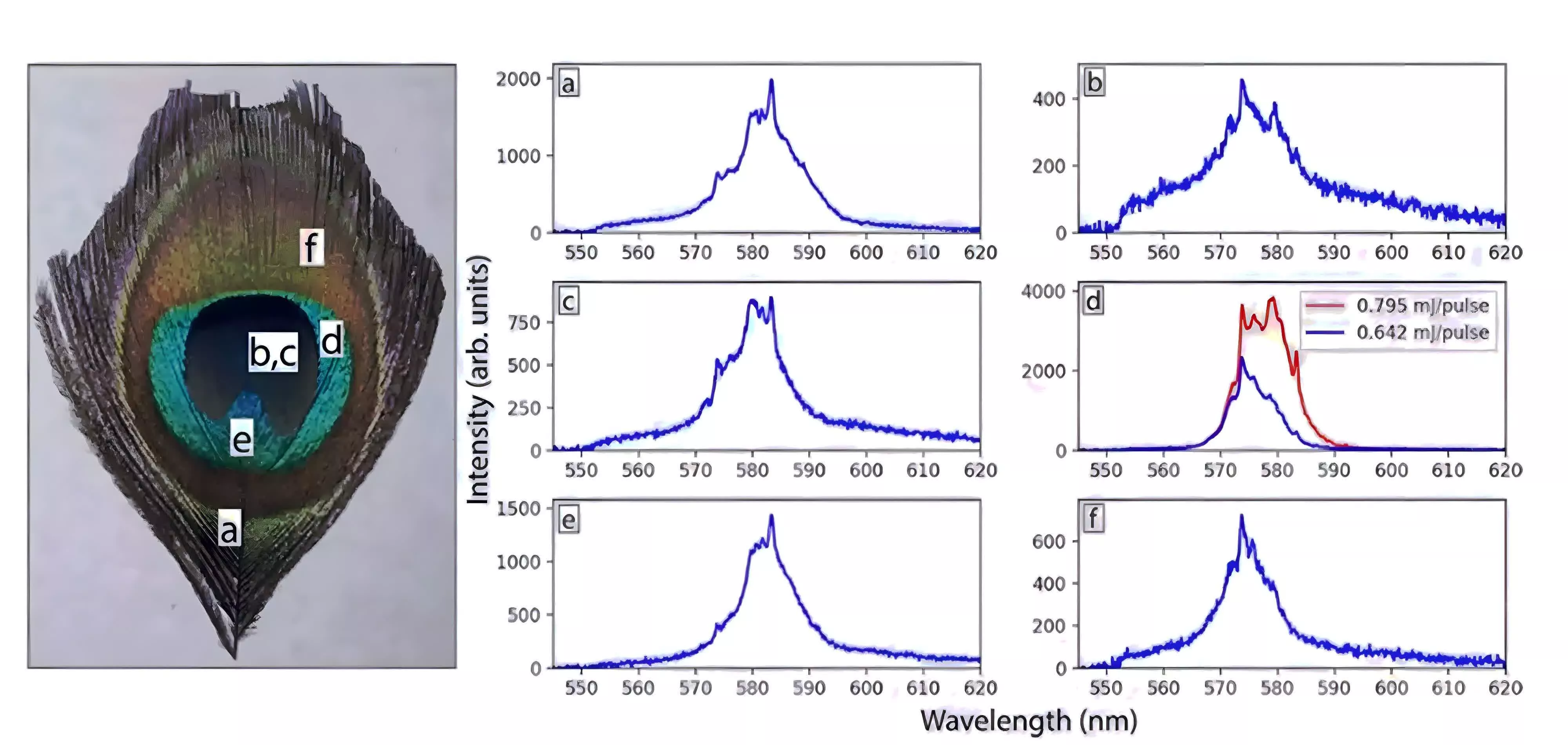
When the laser was aimed toward totally different components of the eyespot, whether or not they appeared blue, inexperienced, yellow, or brown, the researchers discovered sharp, constant laser emission peaks, particularly at wavelengths of 574nm and 583nm. These strains stood out towards the broader fluorescence of the dye and appeared in all feather samples and coloration areas examined, indicating a repeatable and secure impact.
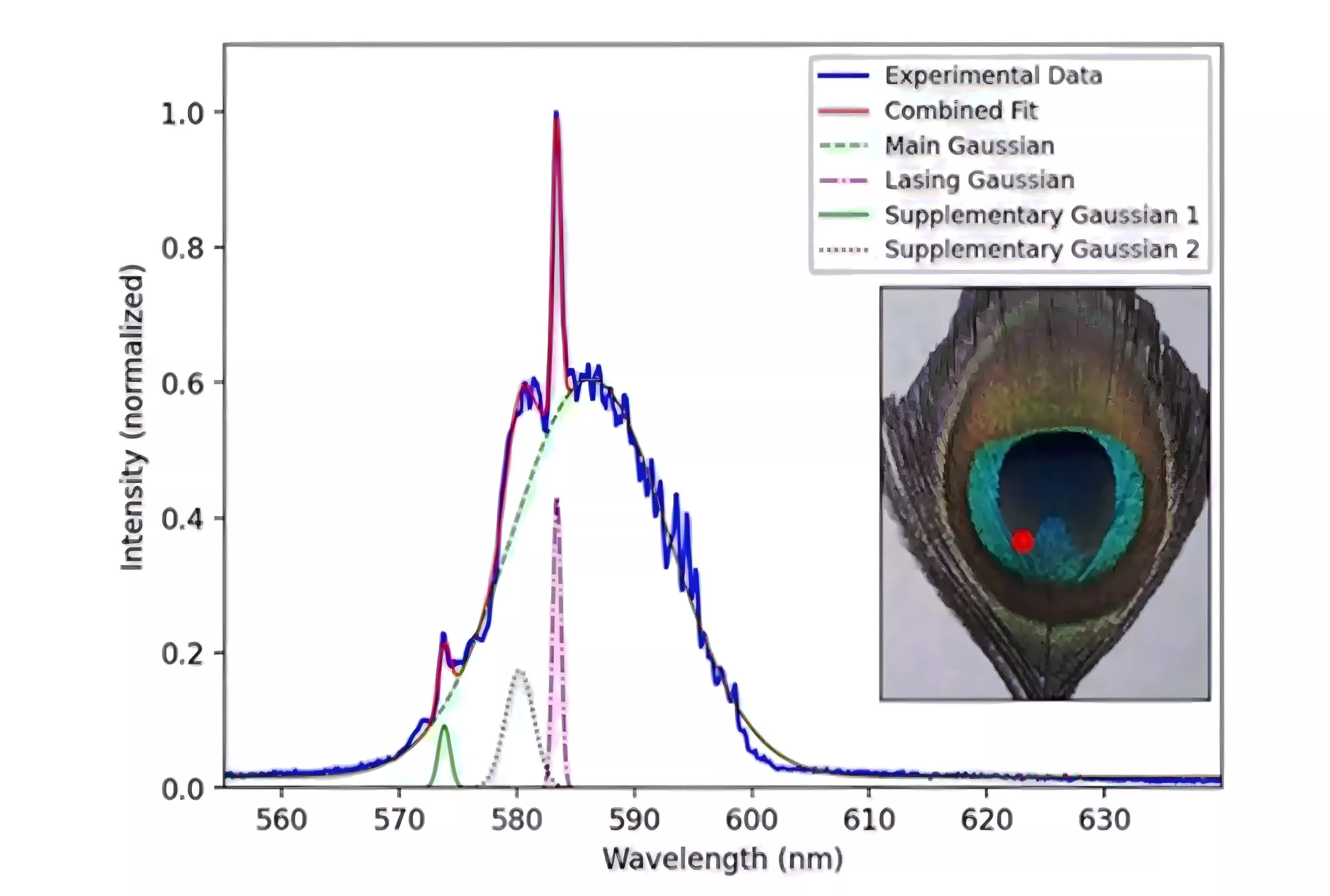
The researchers analyzed the emission spectra and located that the noticed laser conduct did not match expectations for so-called random lasers, which often come up from irregular, extremely scattering environments and generate much less predictable, variable emission strains. As a substitute, the peacock feathers produced constant modes at particular wavelengths, whatever the native coloration or construction, prompting the workforce to conclude that the laser suggestions mechanism was not the identical as that liable for the feathers’ iridescent colours.
Superior evaluation of the spectral strains instructed that the suggestions almost definitely comes from common mesoscale constructions, which persist all through the eyespot, throughout the feather barbules, not from long-range photonic crystal ordering or randomly dispersed scattering paths. The examine dominated out different explanations equivalent to whispering gallery mode lasers, which might require exact round cavities not naturally present in peacock feathers.
The lasing impact additionally required comparatively excessive pump intensities near, or simply above, these present in random laser experiments, however the secure and repeatable nature of the emission factors to an underlying order within the organic microstructure. The outcomes collectively present that pure polycrystalline or heterogeneous supplies, as soon as infused with the best molecules and subjected to applicable remedy, can reveal hidden regularities by means of laser emission.
Though sensible functions stay speculative, the findings recommend a brand new solution to probe the inner group of complicated organic supplies by measuring their laser emission spectra after dye infusion. Utilizing this system, it could someday turn into doable to map or characterize “hidden” structural motifs, or cavities, inside feathers and different tissues, opening up alternatives for analysis in supplies science, biophotonics, and bio-inspired laser applied sciences. For instance, Nathan Dawson of Florida Polytechnic College instructed Ars Technica that the analysis may assist create protected, biocompatible lasers for inside use within the human physique in sensing, imaging, and remedy.